Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as strings, return the product of num1 and num2, also represented as a string.
Note: You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to integer directly.【The sadest things which I can found the fastest soultion in leetcode break this rule.】
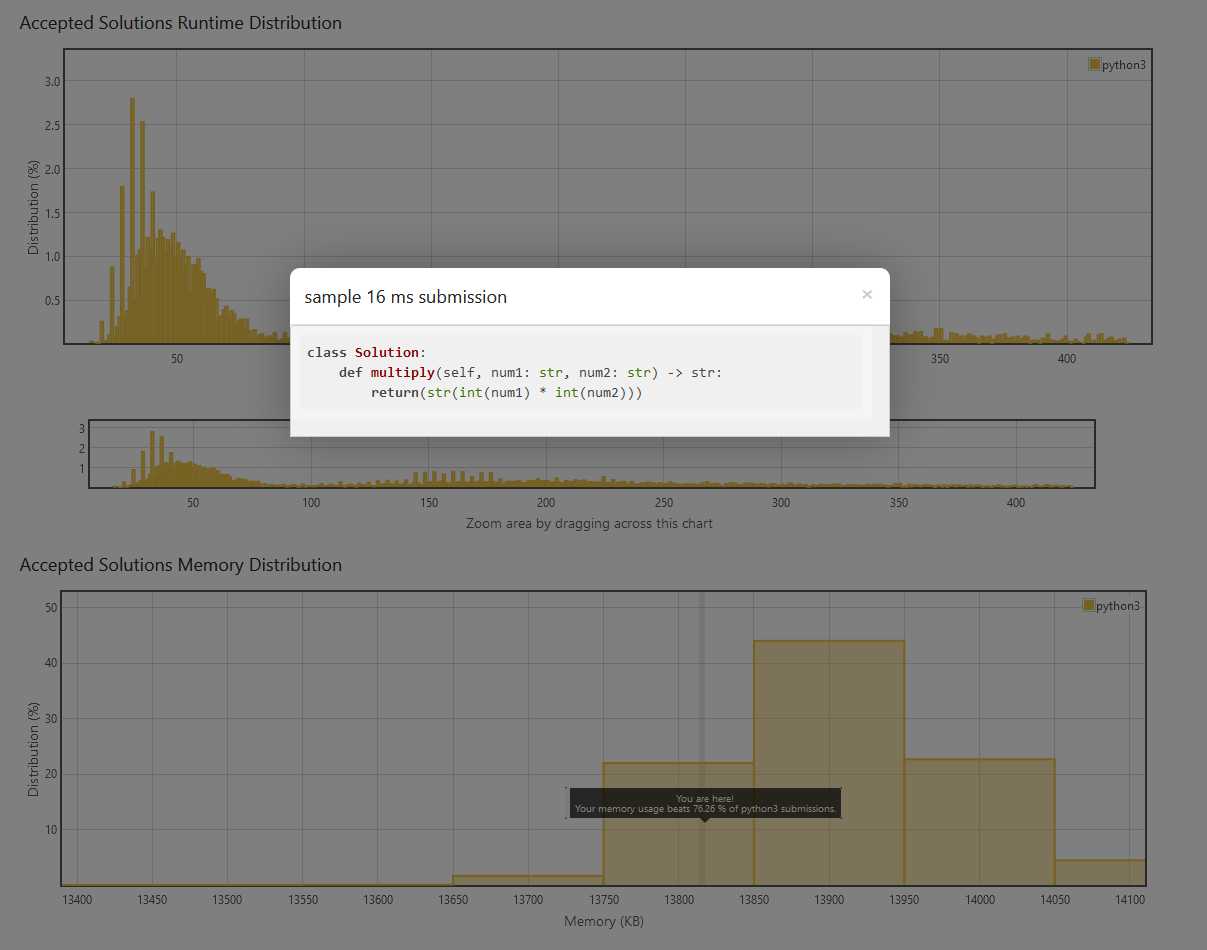
Solution
- submit code
class Solution:
def multiply(self, num1: str, num2: str) -> str:
#return str(eval(num1 + "*" + num2))
# base case
if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0":
return "0"
ret = [0] * (len(num1) + len(num2))
i = len(num1) - 1
while i >= 0:
j = len(num2) - 1
while j >= 0:
mul = int(eval(num1[i] + "*" + num2[j]))
p1 = i + j
p2 = i + j + 1
sum = int(ret[p2]) + mul
ret[p2] = sum % 10
ret[p1] = int(ret[p1]) + int(sum / 10)
j -= 1
i -= 1
# remove the leading 0
while ret[0] == 0:
ret = ret[1:]
res = ""
for i in ret:
res += str(i)
return res
- full code
class Solution:
def multiply(self, num1, num2):
#return str(eval(num1 + "*" + num2))
# base case
if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0":
return "0"
ret = [0] * (len(num1) + len(num2))
i = len(num1) - 1
while i >= 0:
j = len(num2) - 1
while j >= 0:
mul = int(eval(num1[i] + "*" + num2[j]))
p1 = i + j
p2 = i + j + 1
sum = int(ret[p2]) + mul
ret[p2] = sum % 10
ret[p1] = int(ret[p1]) + int(sum / 10)
j -= 1
i -= 1
# remove the leading 0
while ret[0] == 0:
ret = ret[1:]
res = ""
for i in ret:
res += str(i)
return res
S = Solution()
print(S.multiply("12", "456"))

Leave a Reply